Delving into the Depths of Windows 10’s Fast Startup: A Comprehensive Guide to Disabling It
Related Articles: Delving into the Depths of Windows 10’s Fast Startup: A Comprehensive Guide to Disabling It
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Delving into the Depths of Windows 10’s Fast Startup: A Comprehensive Guide to Disabling It. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Delving into the Depths of Windows 10’s Fast Startup: A Comprehensive Guide to Disabling It
Windows 10’s Fast Startup feature, designed to accelerate system boot times, has become a staple for many users. However, it is not without its drawbacks. This feature, which essentially places the system in a hybrid sleep state upon shutdown, can sometimes interfere with specific tasks or applications, leading to unexpected behavior. Understanding the intricacies of Fast Startup and the potential implications of disabling it is crucial for users seeking optimal system performance and troubleshooting specific issues.
Understanding the Mechanics of Fast Startup
Fast Startup is a hybrid approach to system shutdown. Unlike traditional shutdown, where all data is written to disk and the system powers down completely, Fast Startup utilizes a combination of hibernation and shutdown. The operating system kernel and essential drivers are written to a special hibernation file, while the rest of the system is powered down. This allows for a faster boot time as the system can quickly load the kernel and drivers from the hibernation file instead of going through the entire boot process.
Potential Issues Arising from Fast Startup
While Fast Startup offers a noticeable performance boost, it can sometimes lead to complications, particularly in scenarios involving:
- Troubleshooting and Diagnostics: Disabling Fast Startup is often recommended when troubleshooting system issues, as it allows for a clean boot environment free from the potential interference of the hibernation file. This is particularly important when dealing with hardware conflicts, driver errors, or system instability.
- System Updates and Upgrades: Fast Startup can sometimes interfere with system updates and upgrades. The hibernation file might contain outdated system files, potentially causing conflicts during the update process. Disabling Fast Startup ensures a clean slate for updates and upgrades, minimizing the risk of errors.
- Data Recovery and Forensic Analysis: Fast Startup can complicate data recovery efforts and forensic analysis. The hibernation file, containing a snapshot of the system’s state, can obscure data that might be crucial for recovery or investigation. Disabling Fast Startup allows for a more complete and accurate analysis of system data.
- Compatibility with Certain Applications: Some applications, especially those relying on specific system states or interacting directly with hardware, might not function correctly with Fast Startup enabled. Disabling Fast Startup can resolve compatibility issues and ensure smooth operation of these applications.
- Security Concerns: While not widely discussed, some security experts argue that Fast Startup can potentially expose the system to vulnerabilities. The hibernation file, containing a snapshot of the system’s memory, could theoretically be exploited by malicious actors. While the risk is relatively low, disabling Fast Startup can be a precautionary measure for security-conscious users.
Disabling Fast Startup: A Step-by-Step Guide
Disabling Fast Startup is a relatively straightforward process that can be accomplished through the Windows Control Panel. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
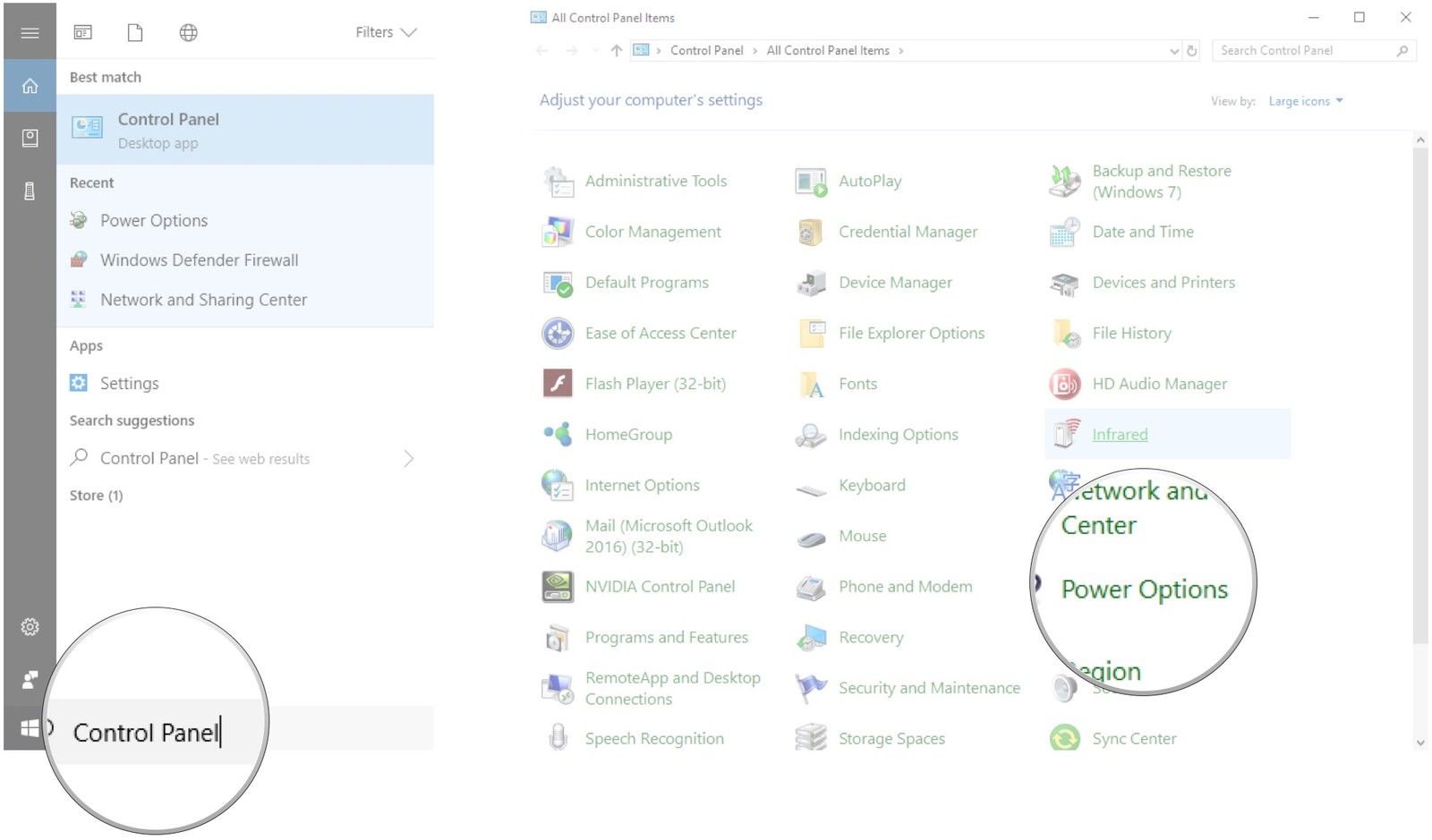
- Access the Control Panel: Open the Control Panel by searching for it in the Windows search bar.
- Navigate to Power Options: In the Control Panel window, locate and click on "Power Options."
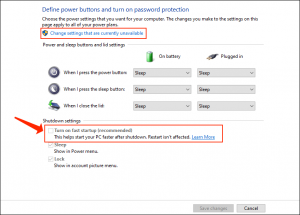
- Select "Choose what the power buttons do": On the left-hand side of the Power Options window, click on "Choose what the power buttons do."
- Change Settings That Are Currently Unavailable: At the bottom of the window, click on the link "Change settings that are currently unavailable."
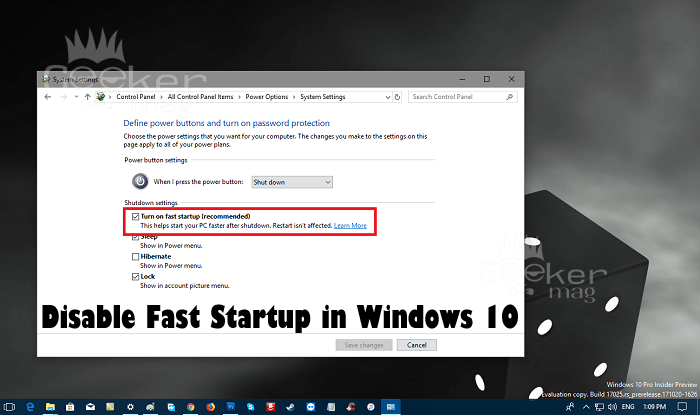
- Disable Fast Startup: Uncheck the box labeled "Turn on fast startup (recommended)."
- Save Changes: Click on "Save Changes" to apply the modifications.
FAQ: Addressing Common Queries
Q: Will disabling Fast Startup significantly impact boot times?
A: Disabling Fast Startup will likely increase boot times slightly, but the difference is usually minimal, especially on modern systems with solid-state drives (SSDs).
Q: Is disabling Fast Startup necessary for all users?
A: Disabling Fast Startup is generally not required for most users. It is primarily recommended for troubleshooting, updating, or when encountering specific compatibility issues.
Q: Will disabling Fast Startup affect other system settings?
A: Disabling Fast Startup solely affects the system’s shutdown behavior and should not impact other system settings.
Q: Can I re-enable Fast Startup after disabling it?
A: Yes, you can re-enable Fast Startup at any time by following the same steps outlined above and checking the "Turn on fast startup (recommended)" box.
Tips for Optimizing System Performance
While disabling Fast Startup can address specific issues, it is essential to consider other factors that can impact system performance:
- Disk Defragmentation: Regularly defragmenting the hard drive can optimize file access times and improve system performance.
- System Updates: Keeping the operating system and drivers up to date ensures optimal compatibility and performance.
- Background Processes: Minimizing unnecessary background processes can free up system resources and enhance responsiveness.
- Clean Up Disk Space: Regularly cleaning up disk space by removing temporary files and unused programs can improve system performance.
Conclusion: Balancing Performance and Functionality
Disabling Fast Startup is a powerful tool for troubleshooting and addressing specific issues. However, it is important to understand the potential impact on boot times and carefully consider whether it is necessary for your specific needs. By weighing the benefits of disabling Fast Startup against the potential downsides, users can make informed decisions to optimize their system’s performance and functionality.




![How To Disable Fast Startup In Windows 10 [Tutorial] - YouTube](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/fRKRSsoXTEQ/maxresdefault.jpg)
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Delving into the Depths of Windows 10’s Fast Startup: A Comprehensive Guide to Disabling It. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!