Addressing High Disk Usage in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Addressing High Disk Usage in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Addressing High Disk Usage in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Addressing High Disk Usage in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide
![How To Fix High Disk Usage in Windows 10 [Solved] - YouTube](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/JFe_dl8-lyU/maxresdefault.jpg)
High disk usage in Windows 10 can significantly impact system performance, leading to sluggish responsiveness, application freezes, and overall frustration. Understanding the root causes and implementing appropriate solutions is crucial for restoring optimal system functionality. This article provides a comprehensive guide to identifying and resolving high disk usage issues in Windows 10.
Understanding the Problem:
Disk usage refers to the amount of data being written to or read from the hard drive or solid-state drive (SSD). When disk usage consistently reaches 100%, the system becomes overwhelmed, as it struggles to process the vast amount of data requests. This leads to a noticeable slowdown in performance, as applications and processes compete for limited resources.
Common Causes of High Disk Usage:
- Background Processes: Numerous applications and system services run silently in the background, consuming disk resources. These processes can include updates, antivirus scans, indexing services, and cloud synchronization.
- Defragmentation: While less common with SSDs, fragmented hard drives can lead to increased disk access times, resulting in high disk usage.
- Insufficient Memory (RAM): When RAM is insufficient, the system relies heavily on the hard drive as a temporary storage space, known as "paging," leading to increased disk activity.
- Disk Errors: Corrupted sectors or bad blocks on the hard drive can cause the system to spend excessive time trying to access data, contributing to high disk usage.
- Malware or Viruses: Malicious software can actively utilize disk resources, performing unauthorized operations and consuming system resources.
- Hardware Issues: Failing hard drives or SSDs can exhibit erratic behavior, leading to increased disk access and high usage.
- Overloaded System: A system with numerous applications running simultaneously, especially resource-intensive programs, can easily overwhelm the disk, resulting in high usage.
Troubleshooting Steps:
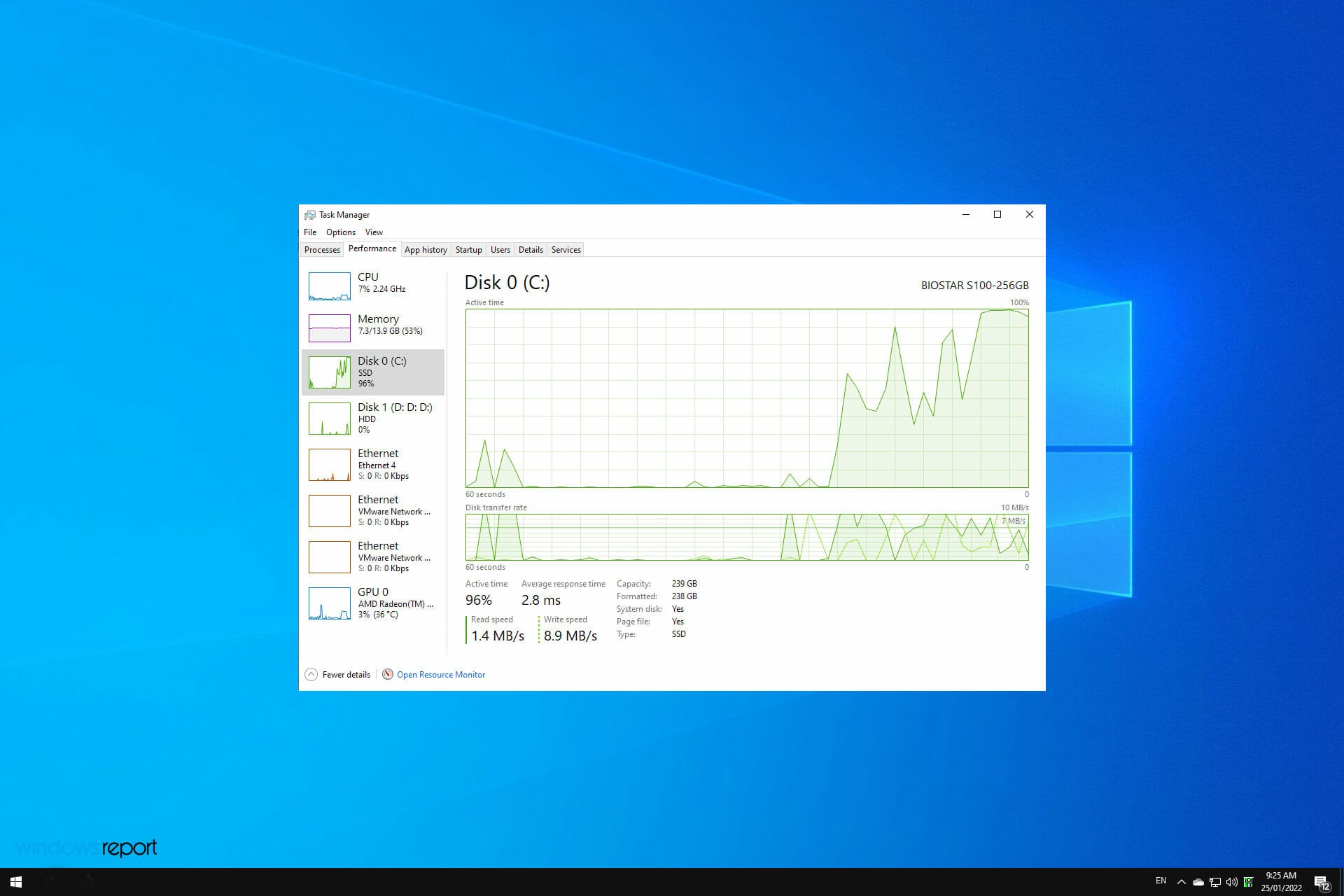
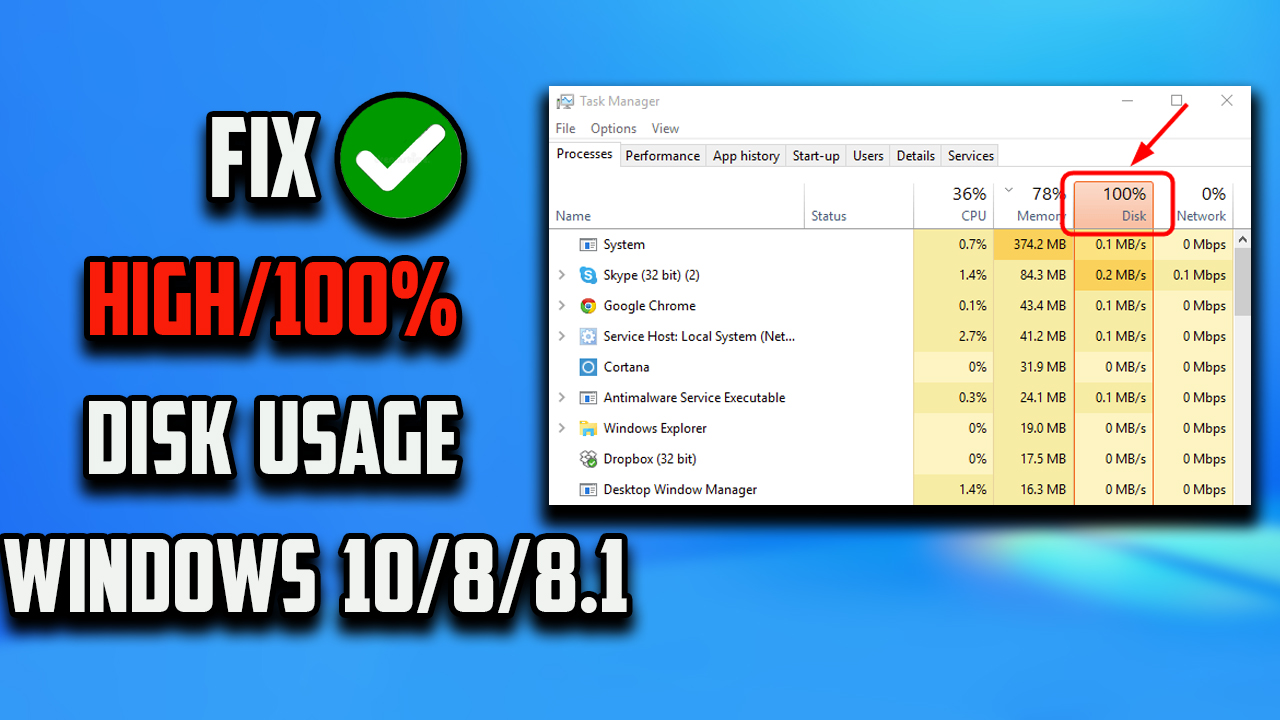
- Task Manager Analysis: The Task Manager provides detailed information about disk usage, identifying the processes consuming the most resources. Open Task Manager (Ctrl+Shift+Esc), navigate to the "Performance" tab, and select "Disk" to view disk usage statistics.
- Identifying Resource-Intensive Processes: In the Task Manager’s "Processes" tab, sort by "Disk" to identify processes with high disk usage. Right-click on a process and select "End Task" to temporarily stop it. Be cautious, as ending essential system processes can lead to instability.
- Disabling Unnecessary Background Processes: Review the "Startup" tab in Task Manager to identify applications that automatically launch at startup, potentially contributing to high disk usage. Disable unnecessary startup programs to reduce system load.
- Windows Updates and Antivirus Scans: Windows updates and antivirus scans often consume significant disk resources. Schedule these tasks for off-peak hours to minimize their impact on performance.
- Check for Disk Errors: Use the "chkdsk" command in Command Prompt (CMD) to scan for and repair disk errors. Open CMD as administrator, type "chkdsk /f /r C:" (replacing "C:" with your system drive letter), and press Enter.
- Defragmentation: If using a hard drive, defragmentation can improve performance by organizing data more efficiently. Open "This PC," right-click on the system drive, select "Properties," then "Tools," and finally "Optimize."
- Optimize System Performance: Adjust Windows settings to prioritize performance over visual effects. Open "Control Panel," select "System and Security," then "System," and click on "Advanced system settings." In the "Performance" tab, choose "Adjust for best performance."
- Free Up Disk Space: Delete unnecessary files, empty the Recycle Bin, and uninstall unused programs to free up disk space.
- Monitor Resource Utilization: Use performance monitoring tools like Resource Monitor or third-party utilities to track disk usage and identify potential bottlenecks.
- Hardware Upgrade: Consider upgrading to a faster SSD or increasing RAM if the existing hardware is insufficient to handle the workload.
FAQs:
Q: Why is my disk usage high even after restarting my computer?
A: Restarting the computer often clears temporary files and processes, but high disk usage might persist due to background processes, scheduled tasks, or underlying system issues.
Q: How do I identify the specific process causing high disk usage?
A: Utilize the Task Manager’s "Processes" tab, sorted by "Disk" to pinpoint the process consuming the most disk resources.
Q: Is high disk usage always a problem?
A: High disk usage during specific tasks like installing software, downloading large files, or running demanding applications is normal. However, persistently high disk usage indicates potential issues.
Q: Can I disable Windows updates to reduce disk usage?
A: Disabling Windows updates is not recommended, as it leaves your system vulnerable to security risks. Instead, schedule updates for off-peak hours to minimize impact.
Q: What are some common symptoms of high disk usage?
A: Slow application loading times, program freezes, sluggish responsiveness, and overall system slowdowns are common symptoms.
Tips:
- Regularly monitor disk usage: Use Task Manager or performance monitoring tools to track disk activity and identify potential issues early.
- Optimize background processes: Disable unnecessary background processes and schedule resource-intensive tasks for off-peak hours.
- Regularly clean up disk space: Delete unnecessary files, empty the Recycle Bin, and uninstall unused programs to free up disk space.
- Perform regular maintenance: Run disk checks, defragmentation (for hard drives), and system updates to ensure optimal performance.
- Consider a hardware upgrade: If the current hardware is insufficient, upgrading to a faster SSD or increasing RAM can significantly improve performance.
Conclusion:
High disk usage in Windows 10 can significantly impact system performance, leading to frustration and productivity loss. By understanding the underlying causes and implementing the troubleshooting steps outlined in this article, users can effectively identify and resolve high disk usage issues, restoring optimal system performance and ensuring a smooth computing experience. It is crucial to remember that addressing high disk usage requires a systematic approach, involving analysis, optimization, and potentially hardware upgrades to ensure a long-term solution.

![How To Fix High Disk Usage in Windows 10 [2020 Solution]](https://benisnous.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/10/How-To-Fix-High-Disk-Usage-in-Windows-10-2020.jpg)


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/how-to-fix-100-disk-usage-in-windows-10-4583918-2-5c3d47fd46e0fb00015065c9.png)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Addressing High Disk Usage in Windows 10: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!