Accelerating Windows 11: Understanding and Utilizing Fast Startup
Related Articles: Accelerating Windows 11: Understanding and Utilizing Fast Startup
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Accelerating Windows 11: Understanding and Utilizing Fast Startup. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Accelerating Windows 11: Understanding and Utilizing Fast Startup
Windows 11, like its predecessors, strives to provide a seamless and efficient user experience. One of the key features contributing to this objective is Fast Startup, a technology designed to significantly reduce the time it takes for your computer to boot up and become operational. This article delves into the intricacies of Fast Startup, its benefits, potential drawbacks, and how to effectively manage its settings for optimal performance.
What is Fast Startup?
Fast Startup is a hybrid approach to system startup, combining elements of traditional hibernation and cold booting. When enabled, the system does not fully shut down upon powering off. Instead, it saves the current state of the operating system and applications to a hibernation file, known as a "hiberfil.sys" file. This file is stored on the system drive and contains the necessary information to restore the system to its previous state quickly.
How Fast Startup Works:
When you initiate a shutdown with Fast Startup enabled, the following steps occur:
- Active Applications are Closed: All running programs are closed, similar to a regular shutdown.
- System State is Saved: The operating system kernel and device drivers are loaded into the hibernation file.
- Power is Reduced: The computer enters a low-power state, similar to hibernation.
Upon restarting, instead of going through the entire boot process, the system:
- Loads the Hiberfil.sys: The system retrieves the saved state from the hibernation file.
- Restores Applications: The saved applications and system state are restored, allowing for a much faster startup.
Benefits of Fast Startup:
- Reduced Boot Time: This is the most significant advantage of Fast Startup. By skipping the traditional boot process, the system can start up significantly faster, saving valuable time for users.
- Improved Responsiveness: The saved system state allows for faster application loading and system responsiveness, leading to a smoother user experience.
- Power Savings: Fast Startup consumes less power compared to a traditional cold boot, contributing to battery life preservation on laptops.
Potential Drawbacks of Fast Startup:
- Increased Disk Space Consumption: The hibernation file ("hiberfil.sys") can occupy significant disk space, especially for systems with large amounts of RAM.
- Compatibility Issues: Some legacy applications or drivers may not function correctly with Fast Startup enabled.
- Security Concerns: In rare cases, Fast Startup can create vulnerabilities, particularly if the hibernation file is compromised.
Managing Fast Startup Settings:
-
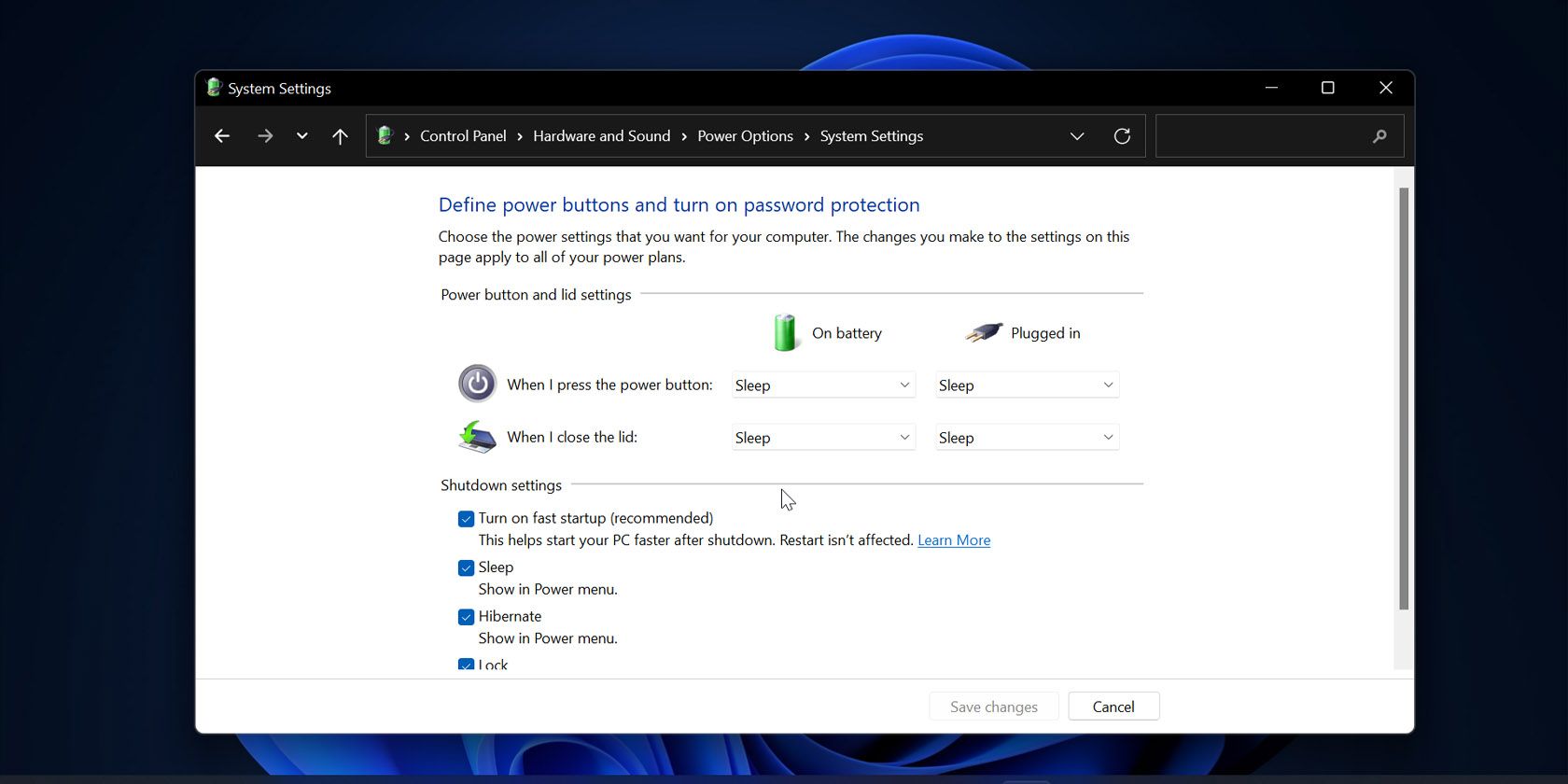
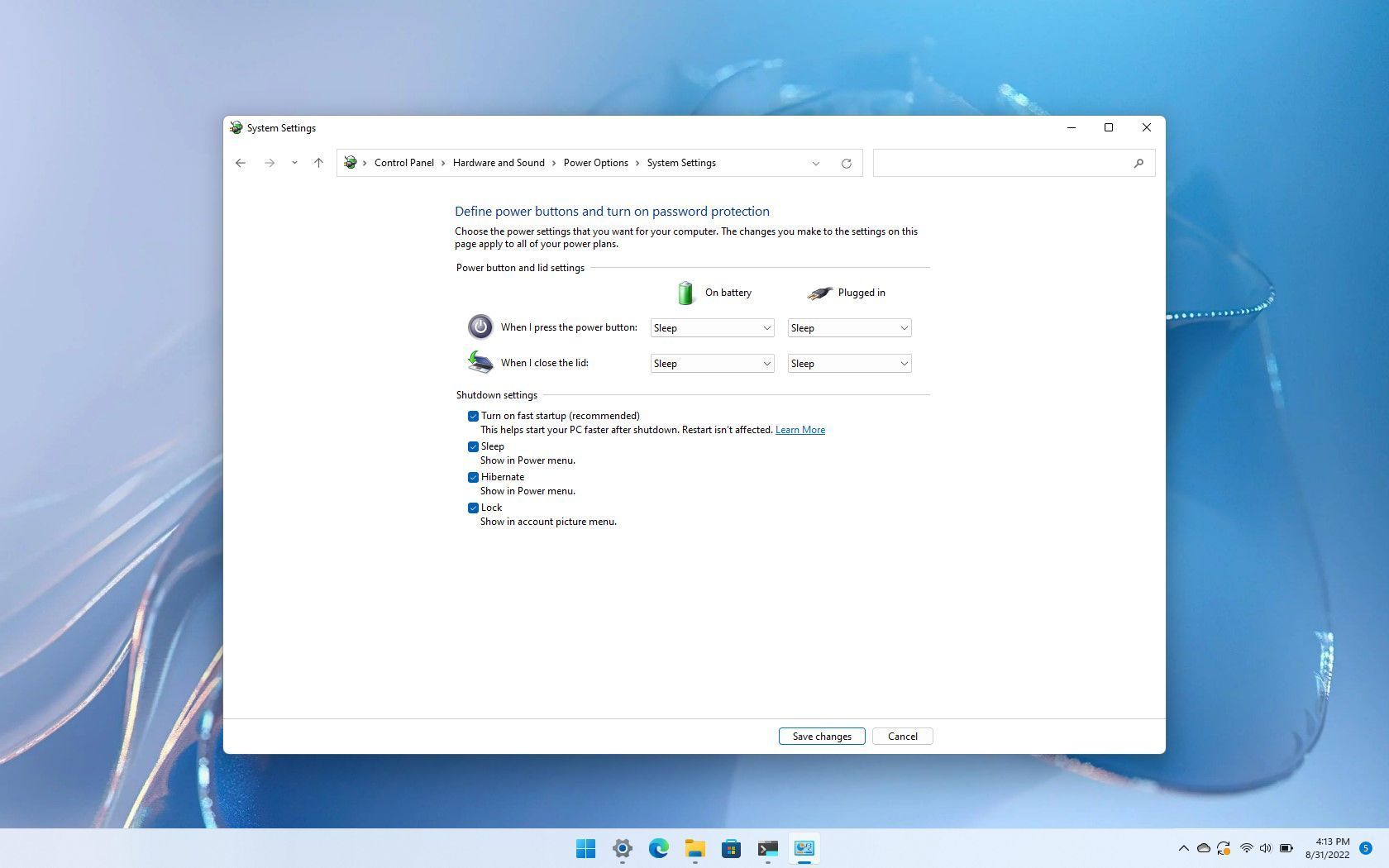
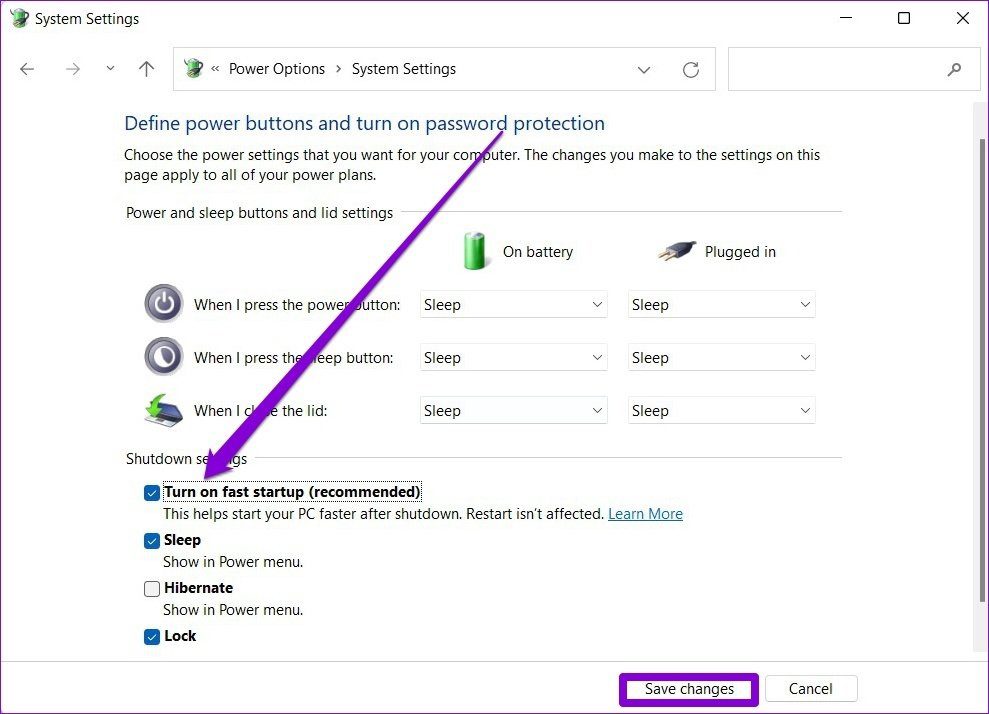
Enabling Fast Startup:
- Open Control Panel and navigate to Power Options.
- Select Choose what the power buttons do.
- Click on Change settings that are currently unavailable.
- Under Shutdown settings, check the box for Turn on fast startup (recommended).
- Click Save changes.
-
Disabling Fast Startup:
- Follow the same steps as above, but uncheck the box for Turn on fast startup (recommended).
- Click Save changes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Q: Is Fast Startup always beneficial?
A: While Fast Startup offers significant advantages, its suitability depends on individual needs and system configuration. If disk space is a concern or compatibility issues arise, disabling Fast Startup might be preferable.
Q: Can I use Fast Startup with hibernation?
A: No, Fast Startup and hibernation are mutually exclusive. Enabling Fast Startup disables the hibernation feature.
Q: What happens to open files and programs when I shut down with Fast Startup?
A: All unsaved data in open files and programs is lost when you shut down with Fast Startup, just like a traditional shutdown.
Q: Is Fast Startup secure?
A: Fast Startup is generally considered secure, but potential vulnerabilities exist if the hibernation file is compromised. It’s important to maintain a secure system environment and implement appropriate security measures.
Tips for Optimizing Fast Startup:
- Keep Your System Clean: Regularly remove unnecessary files and programs to reduce the size of the hibernation file and improve system performance.
- Defragment Your Hard Drive: Defragmenting your hard drive can improve the read and write speeds of the hibernation file, leading to faster startup times.
- Disable Unnecessary Startup Programs: Programs that launch automatically during startup can slow down the boot process. Disable unnecessary programs to minimize startup time.
- Monitor Disk Space: Regularly check the size of the hibernation file ("hiberfil.sys") and consider disabling Fast Startup if it occupies excessive disk space.
Conclusion:
Fast Startup is a valuable feature in Windows 11 that significantly improves the boot time and overall system responsiveness. By understanding its operation and potential drawbacks, users can effectively manage its settings to optimize their system’s performance. While Fast Startup offers numerous benefits, users should be aware of its limitations and adjust their settings accordingly. By balancing the advantages and disadvantages, users can harness the power of Fast Startup to enhance their Windows 11 experience.
![How to Enable or Turn On Fast Startup on Windows 11 [Tutorial] - YouTube](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/aO2eIvIHUlU/maxresdefault.jpg)





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Accelerating Windows 11: Understanding and Utilizing Fast Startup. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!