Accelerating Windows 10: A Deep Dive into Fast Startup
Related Articles: Accelerating Windows 10: A Deep Dive into Fast Startup
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Accelerating Windows 10: A Deep Dive into Fast Startup. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Accelerating Windows 10: A Deep Dive into Fast Startup
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Accelerating Windows 10: A Deep Dive into Fast Startup
- 3.1 Understanding Fast Startup: A Hybrid Approach to Boot
- 3.2 Benefits of Fast Startup: A Boost in Productivity
- 3.3 Potential Drawbacks: Addressing Concerns and Limitations
- 3.4 Managing Fast Startup: Tailoring to Individual Needs
- 3.5 FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Fast Startup
- 3.6 Tips for Optimizing Fast Startup: Maximizing its Effectiveness
- 3.7 Conclusion: A Powerful Feature for a Smoother Windows 10 Experience
- 4 Closure
Accelerating Windows 10: A Deep Dive into Fast Startup
Windows 10, known for its user-friendly interface and robust features, continuously strives to enhance user experience. One of the notable enhancements introduced in Windows 10 is the "Fast Startup" feature, designed to significantly reduce boot times, allowing users to access their systems faster. This article delves into the intricacies of Fast Startup, exploring its functionalities, benefits, potential drawbacks, and how users can effectively manage it.
Understanding Fast Startup: A Hybrid Approach to Boot
Fast Startup, often mistaken for a simple "quick boot" mode, is a hybrid approach that combines elements of traditional cold boot and hibernation. It differs from a cold boot, where the system starts from scratch, loading all necessary files and drivers. Similarly, it differs from hibernation, where the system’s state is saved to the hard drive, allowing for a quicker resumption.
Fast Startup cleverly bridges the gap by utilizing a "hybrid shutdown" process. When a user chooses to shut down their computer, Fast Startup does not completely power down the system. Instead, it saves the current kernel and device drivers to a hibernation file on the hard drive, while simultaneously shutting down the user session. This partially powered-down state allows for a faster boot, as the system can quickly load the saved kernel and drivers, effectively skipping the lengthy process of loading them from scratch.
Benefits of Fast Startup: A Boost in Productivity
The primary advantage of Fast Startup is the noticeable reduction in boot times. By leveraging the saved kernel and drivers, the system can quickly jumpstart, offering a significantly faster user experience. This translates to increased productivity, as users spend less time waiting for their systems to become operational.
The benefits of Fast Startup extend beyond just faster boot times. It also contributes to:
- Reduced Power Consumption: By skipping the full boot process, Fast Startup consumes less power, particularly during the startup phase. This can be beneficial for users who prioritize energy efficiency.
- Improved System Performance: Fast Startup can lead to improved system performance by reducing the time it takes to load the kernel and drivers, ultimately contributing to a smoother overall user experience.
Potential Drawbacks: Addressing Concerns and Limitations
While Fast Startup offers numerous advantages, it is not without its potential drawbacks. One key concern is the lack of a true "cold boot" during a Fast Startup shutdown. This can lead to lingering issues, particularly if the system encounters errors during the previous session. The saved kernel and drivers may not be completely clean, potentially causing instability or performance problems in the subsequent boot.
Another potential concern is the potential for data corruption. If the hibernation file, where the kernel and drivers are stored, becomes corrupted, it can lead to boot issues or data loss. This is relatively uncommon but serves as a reminder to maintain a reliable backup system.
Furthermore, Fast Startup can impact the functionality of certain applications and utilities that require a clean boot, such as troubleshooting tools or specific diagnostic software. These tools often need a complete system restart to function correctly, and Fast Startup might interfere with their operation.
Managing Fast Startup: Tailoring to Individual Needs
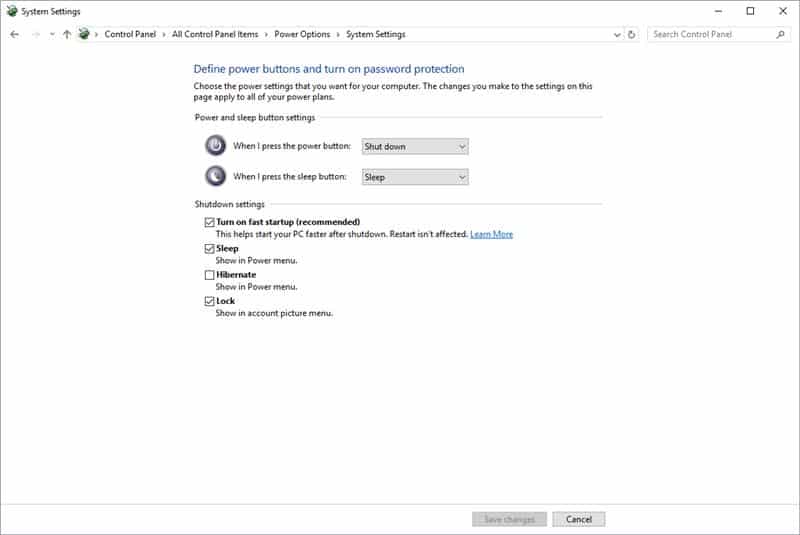
Windows 10 offers users the flexibility to enable or disable Fast Startup based on their individual needs and preferences. Users can easily access these settings through the "Power Options" in the Control Panel.
Enabling Fast Startup:
- Open the Control Panel and navigate to "Power Options."
- Click on "Choose what the power buttons do."
- Click on "Change settings that are currently unavailable."
- Under "Shutdown settings," check the box for "Turn on fast startup (recommended)."
- Click "Save changes" to apply the settings.
Disabling Fast Startup:
- Follow the same steps as above to access the "Shutdown settings."
- Uncheck the box for "Turn on fast startup (recommended)."
- Click "Save changes" to apply the settings.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Fast Startup
1. Is Fast Startup compatible with all versions of Windows 10?
Fast Startup is available in all versions of Windows 10, starting with Windows 10 version 1511 (November Update).
2. Does Fast Startup work on all hardware configurations?
While Fast Startup is generally compatible with most hardware configurations, its effectiveness can vary depending on factors such as the type of hard drive, the amount of RAM, and the overall system performance.
3. Can I use Fast Startup with a dual-boot system?
Fast Startup is generally not recommended for dual-boot systems, as it might interfere with the boot process of the other operating system.
4. How often should I perform a full shutdown instead of using Fast Startup?
It is generally recommended to perform a full shutdown at least once a week to ensure a clean system restart and minimize the risk of potential issues related to the saved kernel and drivers.
5. Does Fast Startup affect the lifespan of my hard drive?
Fast Startup does not directly impact the lifespan of your hard drive. However, frequent writes to the hibernation file can potentially accelerate wear and tear on the drive over time.
Tips for Optimizing Fast Startup: Maximizing its Effectiveness
-
Keep the hibernation file clean: Regularly delete the hibernation file to ensure a clean restart. This can be done through the command prompt by typing "powercfg -h off" and pressing enter.
-
Use a solid-state drive (SSD): SSDs provide significantly faster read and write speeds, enhancing the benefits of Fast Startup.
-
Minimize the number of startup programs: Reducing the number of programs that automatically start with Windows can further improve boot times.
-
Disable unnecessary services: Identifying and disabling unnecessary services can contribute to a faster boot process.
-
Update your drivers: Ensure that all system drivers are up to date to ensure optimal performance and compatibility.
Conclusion: A Powerful Feature for a Smoother Windows 10 Experience
Fast Startup is a powerful feature in Windows 10 that significantly reduces boot times, enhancing user experience and productivity. By leveraging a hybrid approach, it combines the speed of a hibernation boot with the thoroughness of a traditional shutdown. While it offers numerous benefits, users should be aware of potential drawbacks and manage Fast Startup accordingly. By understanding its functionalities and implementing best practices, users can maximize its effectiveness and enjoy a smoother and more efficient Windows 10 experience.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Accelerating Windows 10: A Deep Dive into Fast Startup. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!